Category: All About Guns
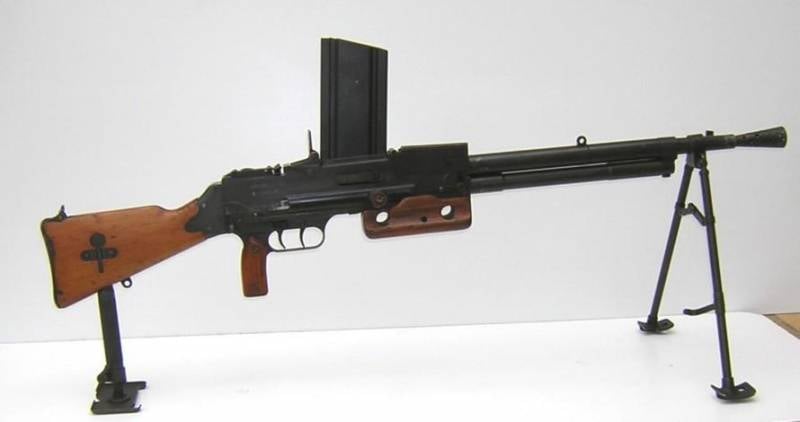



































Machine gun FM Mle 1924/29 “Chatellerault”. Photo littlegun.be
Alexei Tolstoy, Gloomy Morning
stories about weapon. And it so happened that in the early 1900s, Samuel McClean, a doctor by training, abandoned his medical practice at the age of 40 and designed, and even managed to make a large 37-mm automatic gun in metal, which was mounted on a pedestal in the back of a truck. True, he did not succeed with a cannon, and then he began to develop a rifle-caliber machine gun. By 1920, he received more than 30 patents in his name, but his most important achievement was the development of a light machine gun with a gas engine.
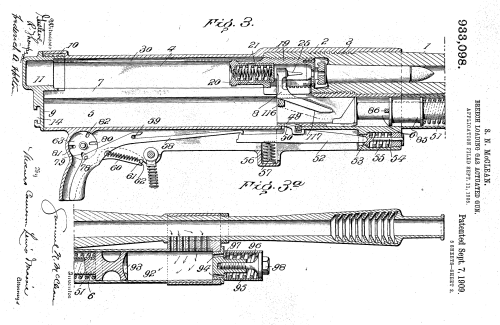
Diagram of a McClean machine gun from a 1909 patent
In 1918-1919, McClean tried to create another light machine gun and … created it, and its main feature was the absence of a fire translator. Instead, without turning around for a long time, he used a pair of triggers: the rear for semi-automatic fire and the front for fully automatic. And although this innovation as a whole did not take root in weapons practice, in a country like France, on the basis of its development, even its own light machine gun was created, replacing the useless Chauchat for many years.

Two triggers – one of the “highlights” of the McClin machine gun. Photo forgottenweapons
The French army took care of the issue of replacing it immediately after the end of the First World War. Considering the situation in which she found herself with the Chauchat completely intolerable, and realizing that you couldn’t win much with heavy machine guns alone, the French military decided to adopt the American Browning Automatic Rifle (BAR), but in the end they still considered more profitable to develop their own weapons.
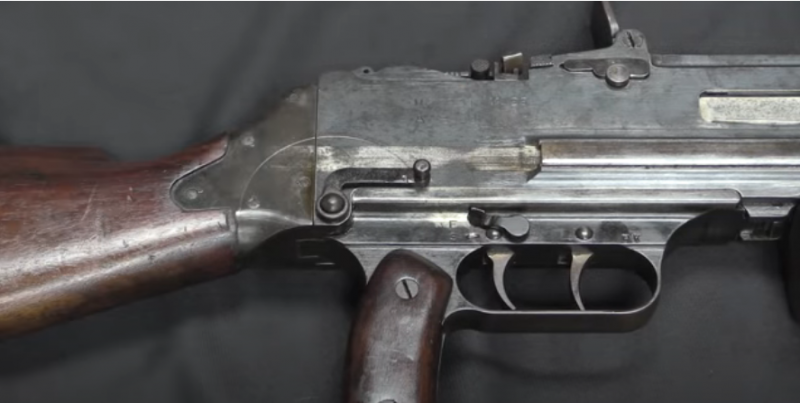

This photo clearly shows a number of distinctive features of the Chatellerault machine gun: on the left – the handle in the rear of the receiver served to facilitate the disassembly of the machine gun, with its help the locking bolt was unscrewed and the butt was separated; above the rear trigger is the safety lever. Photo forgottenweapons
After that, MAS (an abbreviation for Manufacture d’Armes de St. Etienne – one of several state-owned arms factories in France), borrowing something from BAR and something from other samples, created its own light machine gun, developed by Lieutenant Colonel Reibel with the assistance of chief armorer Chosse. Moreover, it was already created under the new 7,5 mm cartridge, which replaced the old 8 mm. So there was a weapon called “Automatic rifle mod. 1924” or Fusil-mitrailleur Mle 1924.

Gas engine, barrel and bolt of the Chatellerault machine gun. Photo littlegun.be
Already at the end of May 1925, FM Mle 1924 was put into mass production and again in May 1926 took part in the battles in Morocco against the reefs. It was immediately well received by the troops, especially since it favorably differed for the better from the Chauchat and was comparable in its characteristics to the much heavier Hotchkiss heavy machine gun. However, the problems with the new 7,5mm cartridge proved to be so significant that the French had to develop the shorter 7,5×54mm cartridge, which from 1929 became the standard for all future rifles and light machine guns in French service. A new modified version of the Fusil-mitrailleur modèle 1924 was named FM Mle 1924/M29 and was mass-produced from 1930. 187 of these machine guns were made, and earlier samples were re-barreled for new 412 × 7,5 mm ammunition.
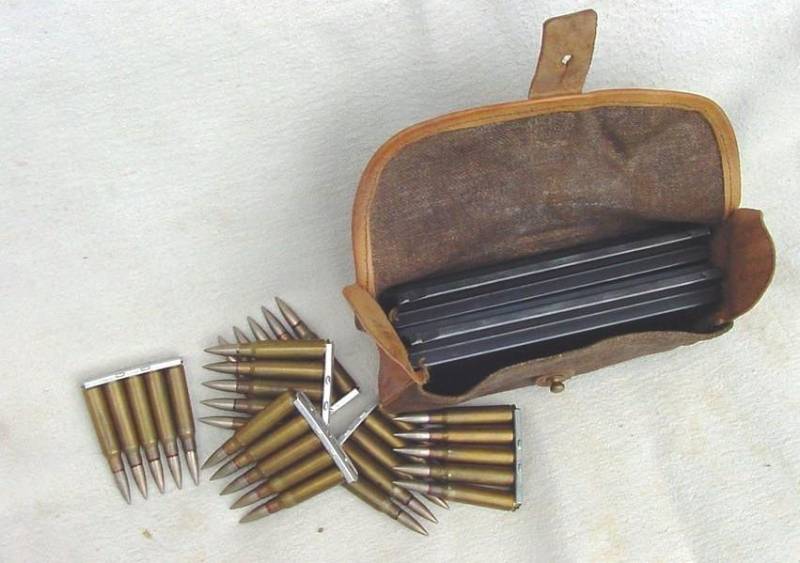

Magazine in a case and clips with 7,5×54mm cartridges. Photo littlegun.be
The new French machine gun took all the best from the models that performed well during the war years, and some later innovations. The machine gun had a 25-round detachable magazine inserted from above, a bolt held by a slide delay after the last cartridge had been fired from the magazine, and two separate triggers, as on an experienced McClean machine gun: a front trigger for single shots and a rear trigger for automatic firing.
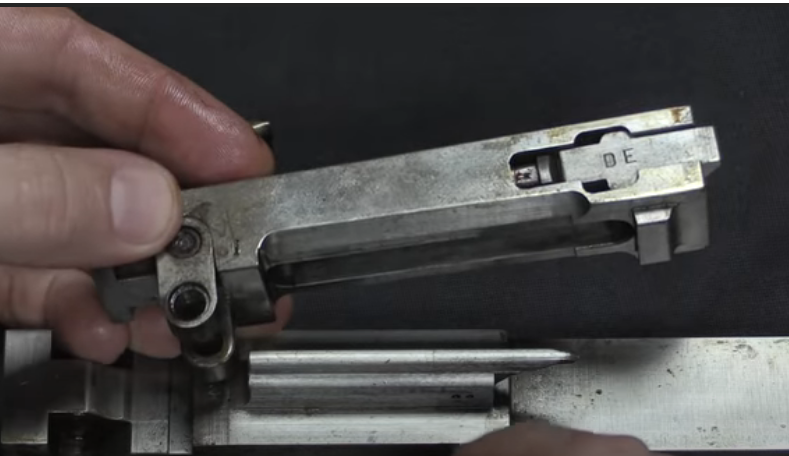

Shutter photo. The locking of the Chatellerault barrel, by analogy with the Browning automatic rifle, was carried out by tilting the bolt in its rear part, where there were two movable earrings on a common axis. When moving forward, the barrel ran into a ledge on the frame at the top and, accordingly, warped, locking the barrel. But the drummer on the vertical stand, as in the Lewis machine gun, was made motionless. Photo forgottenweapons
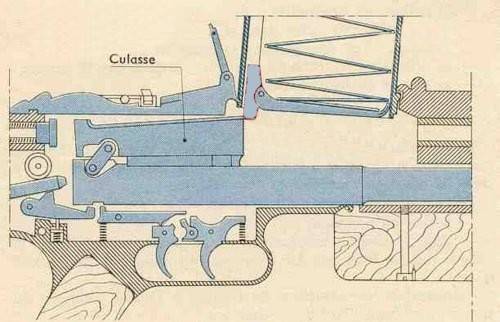
Scheme of the operation of the bolt frame and the bolt of the Chatellerault machine gun. Rice. armesfrancaises.free.fr
The barrel was screwed into the receiver like the Browning Automatic Rifle (BAR), so it could not be quickly and easily replaced in the field, unlike the Czech ZB vz. 26 and its British variant, the Bren machine gun. The operating instructions for the French army (July 1925) recommended not to allow more than 400 shots with continuous fire, since then it took ten to fifteen minutes for the machine gun to cool sufficiently. The optimal firing scheme from the FM 1924 was as follows: shooting four or five detachable magazines (from 100 to 125 rounds), then a short pause – and so on, to ensure stable operation of the machine gun.

Receiver cover in the closed position. Photo forgottenweapons
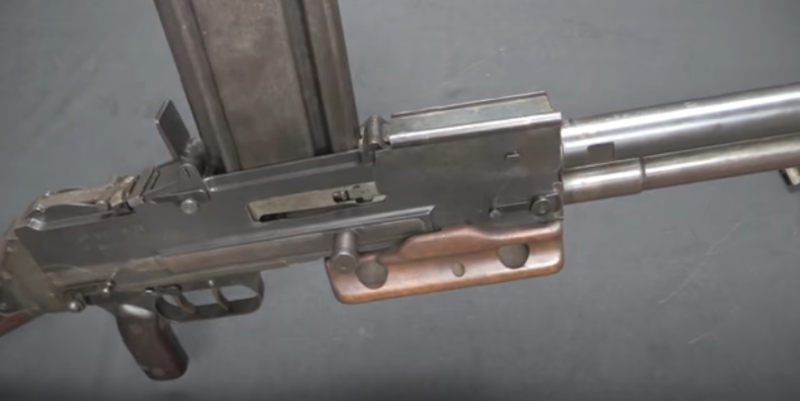

The lid is open, a magazine is inserted into the receiver. Photo forgottenweapons
The protection of all holes on the body of the machine gun from dirt and dust was thought out perfectly. For example, a single cover was provided on the machine gun for the magazine opening and the hole for extracting spent cartridges. The rate of fire was quite high – 450 rounds per minute, which made it possible to shoot for a long time without overheating the barrel. Since the machine gun was created on the basis of the prototype MAC 1923 of the Chatellerault weapons factory, for brevity they began to call it that.

Machine gun with folded bipod. Royal Arsenal, Leeds
As already noted, the design of the machine gun was quite perfect, although not without flaws. So, due to the fact that the store was inserted from the top in the center, the sight had to be shifted to the left, which was inconvenient for left-handers. The side-folding front bipod was strong and light, but swung freely around the barrel rather than being fixed on it, which interfered with marksmanship. The holes on the wooden forearm made it possible to mount it on combat vehicles, which made it possible to use it as a light machine gun. It was also convenient for shooting from a position on the hip.

Machine gun with unfolded bipod. Royal Arsenal, Leeds
The soldiers of the French army really liked the new weapon, who first used it in battle on May 11, 1926 during the Rif War. As a result, the FM 24/29 became the standard automatic weapon of the French infantry and cavalry at the beginning of World War II. After the surrender of France in 1940, the Germans got a great many of these machine guns, as well as cartridges for them. So until the very end of the war, under the designations MG 115 (f) and MG 116 (f), they used them in their troops – in the Wehrmacht and the Volkssturm to defend the Atlantic Wall. MAC 24/29 was also used in limited numbers by the Finnish Defense Forces during the Winter War with the USSR, and then during the years of its participation in World War II. From 1943, when the French army was re-armed and reorganized in North Africa with Allied support, the FM 24/29 remained in service, as French troops considered it superior to the Browning automatic rifle.
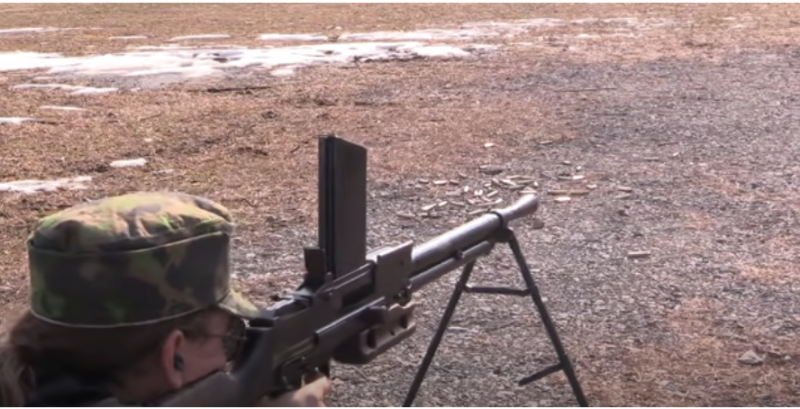

That’s how they shot him lying down. Photo forgottenweapons
There was a modification – “Machine gun arr. 1931″, originally intended for use on the fortifications of the Maginot Line, but later used for weapons tanks and other armored vehicles. This model had a peculiarly shaped stock and a side drum magazine for 150 rounds. The internal structure remained the same as on previous models, however, the barrel length was increased, due to which both the overall length of the machine gun and the muzzle velocity increased. Accordingly, the mass also increased, but since the French used these weapons in stationary positions or on the chassis of wheeled and tracked vehicles, this did not become a problem, and machine guns mod. 1931 in the pre-war period were produced in large quantities.
After the defeat of France in June 1940, the 1931 model of the year also began to be used by the Germans, most often as a tank – Kpfw MG 331 (f), and an anti-aircraft machine gun. The Germans, however, noted that all modifications of the Chatellerault machine gun had a number of shortcomings, primarily related to the cartridge used by the French: in their opinion, it was too low-power for them, so the firing range of them seemed small to them.
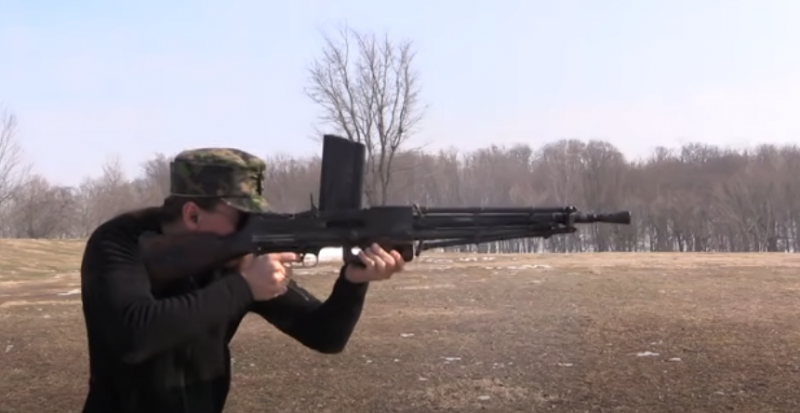

And so – standing! Photo forgottenweapons
As soon as World War II ended, the production of FM 24/29 machine guns was continued, so that during the First Indochina War it became the main workhorse of the French army and was used as an infantry squad weapon, and was put on jeeps modeled on the British SAS. The FM 24/29 was used by the French in Algeria, but it was replaced with the new AA-52 universal machine gun only in the 1960s. However, this did not mean that it was immediately handed over to warehouses.
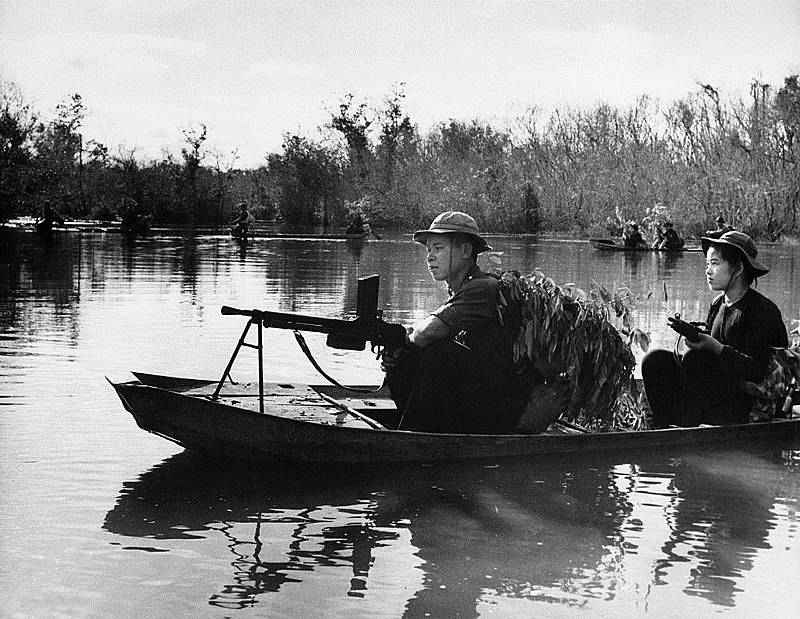

Viet Cong patrol, October 27, 1966
In Southeast Asia, he fought in the armed forces in Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam during the Indochina War. The fighters of the Viet Minh and Viet Cong, the People’s Army of Vietnam and the Army of the Republic of Vietnam were armed with this machine gun. In the Republic of Cambodia, it was used until 1989.
TTX FM 24/29
In service: 1925-1979 (French Army), 1956-2008 (national gendarmerie)
Manufacturer: Manufacture d’Armes de Châtellerault
Produced in 1925-1960s. 232 942 pcs.
Weight: 8,9 kg
Length: 1080 mm
Barrel length: 500 mm
Cartridge: 7,5 × 54 mm
Rate: 450 rounds per minute
Initial speed: 830 m / s
Effective range: 1250 m
Maximum firing range: 3950 m
Penetration: 70 cm of ground at 400 m (cartridge with an ordinary bullet)
Armor penetration: 3 mm steel at 400 m (cartridge with armor-piercing bullet)
Feeding System: 25-round detachable box magazine
- Author:
- Vyacheslav Shpakovsky






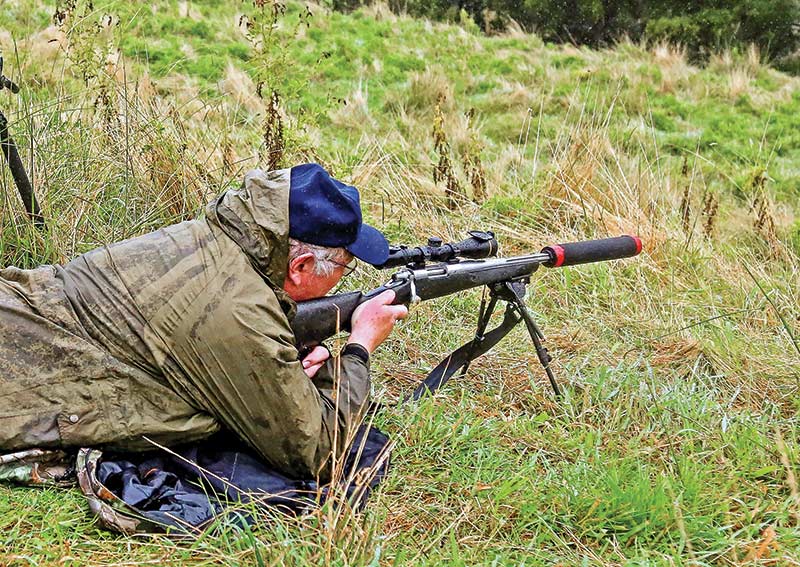
Acquiring “good enough” skill with a rifle, at least adequate for big-game hunting at moderate ranges, is actually not terribly hard. Most game animals are shot at ranges under 200 yards, often considerably less, and generally from some sort of rest. It used to surprise me to find many rifle owners, even those knowledgeable and enthusiastic, had little interest in shooting.
For those who do want to be good rifle shots, learning trigger management is essential. Trigger control is the essence of good shooting, the single most important factor. Good trigger management covers a multitude of sins. Don’t misunderstand, proper form and consistency matter. At the highest levels of shooting, competitors train so every aspect of stance, hold, grip and even breathing are as close to exactly the same as humanly possible for every shot. Yet, none of this matters if the last thing the shooter does is yank the trigger.
Shooting 101
What is good trigger management? It means pressing the trigger straight back, at constantly increasing speed, without imparting movement to the firearm. Simple enough, but making good trigger control a dependable subconscious skill takes thousands of quality repetitions.
Factory rifle trigger pulls have improved dramatically over the past couple of decades. The 1960s and much of the ’70s were actually kind of depressing years for rifle enthusiasts. An era of manufacturing based on skilled hand labor and relatively simple machine tools was coming to an end, as skilled labor became less common and therefore expensive. The marvelous, extremely precise computer-controlled machine tools we have today didn’t yet exist.
Many of we who lived through the era were left permanently scarred. We were certain quality control was a thing of the past and would only get worse. We’re easily identified because we say “pre” all the time; pre-war, pre-’64, pre-1950, pre-lock, pre-number. Everything used to be better, at least so it seemed at the time.
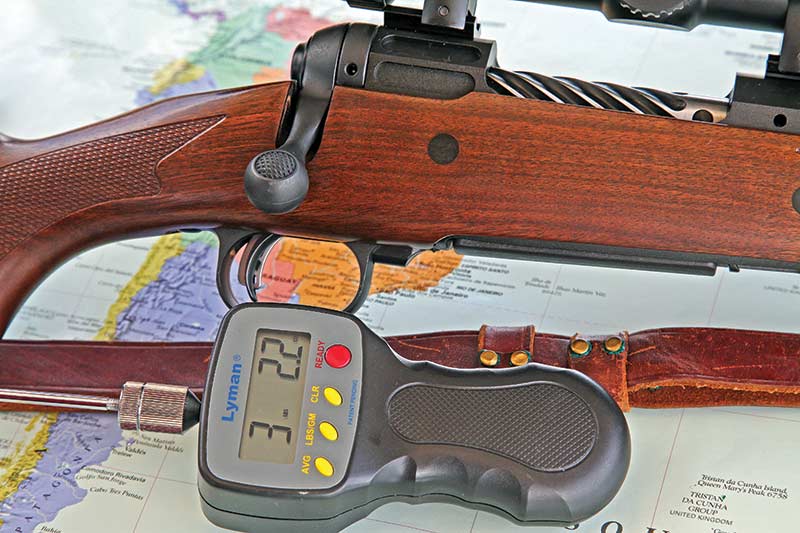
Trigger quality suffered worst of all, partly I suppose because of the growth of consumer litigation and manufacturers’ fear of lawsuits. From a risk avoidance point of view it made sense to make triggers non-adjustable, with plenty of sear engagement and a 6- or 7-lb. weight of pull. The average once-a-year hunter tolerated such pulls as just the way things are. Those who actually shot a lot simply factored in the cost of a trigger job or replacement trigger.
Rifle quality improved, slowly at first, then more quickly as manufacturers began adopting modern techniques such as computer-assisted design and computer-assisted manufacturing. Improvement in trigger quality seemed to come slowly, at least with the bigger American gunmakers. Some European imports and smaller American makers — Dakota Arms and Kimber come to mind — had decent triggers but were expensive and not widely distributed.
The Shot Heard ’Round The Shooting World
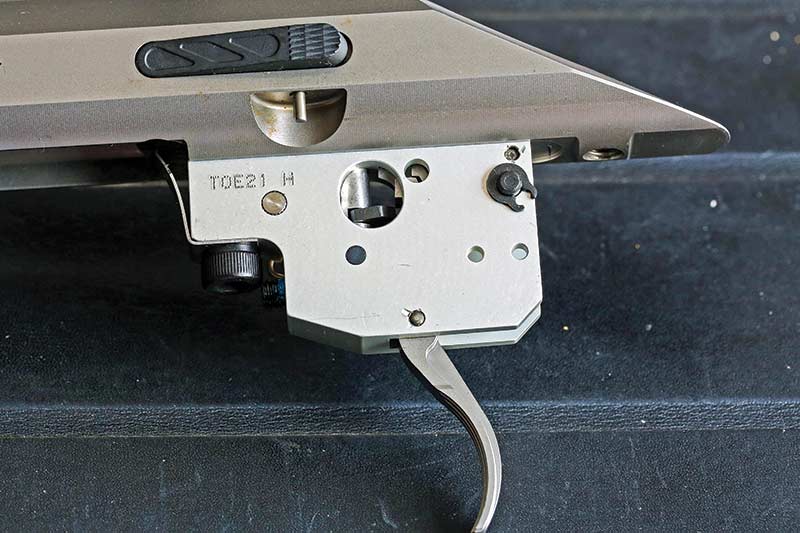
In a just world, the name Ron Coburn would be as famous and revered in the firearms world as names such as Bill Ruger and Sam Colt. Coburn took over leadership of a nearly bankrupt Savage corporation and turned it into an industry giant. Coburn’s genius was in leading and inspiring creative people to design products people wanted, at a price they could afford. Early in the 21st century he challenged his staff to design a trigger with a quality pull, crisp, reasonably light, adjustable, affordable and safe. The result was the Accu-Trigger, which became standard on Savage factory rifles around 2002–2003. Other manufacturers redesigned their triggers so quality pulls were available to every rifle buyer, not just the wealthy and enthusiastic. I think shooters today are fortunate to have rifles with decent triggers widely available at reasonable prices, providing a headstart in learning good habits.
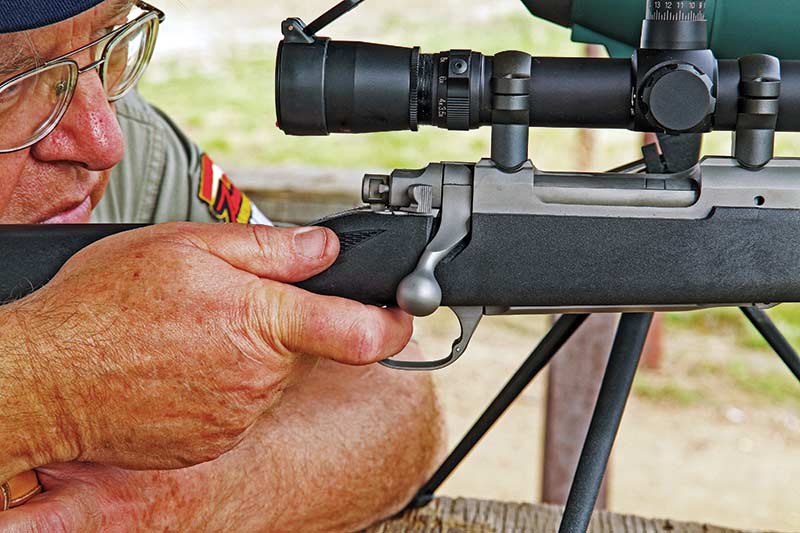
The old saying “practice makes perfect” isn’t always so. Practice makes permanent. The neural paths controlling the muscles don’t judge. They develop through repetition and will learn bad habits as thoroughly as good ones. Over the years, my views have evolved. I’m not as dogmatic about form and style as I once was, but there are basic elements I think are important. One is to have the trigger finger placed squarely across the trigger face so the pressure is straight back, in line with the axis of the bore. I’ve become more conscious of avoiding any side pressure on the trigger.
I like to have the trigger finger more or less in line with the bore, not angled diagonally as seems to happen with many pistol grip shapes. I keep the thumb of the shooting hand on the right side of the stock rather than wrapped around the pistol grip. This allows a lower grip so the trigger finger doesn’t have to be on a diagonal angle.
It also encourages a light touch with the shooting hand. I find a light touch is more consistent, less prone to “steering” the gun or applying side pressure, plus it allows the trigger finger to move independently. Years ago I thought differently and who knows, I may think differently in the future. But today this is what feels right and more importantly, performs right for me.
















The sales of firearms, especially AR-15-style rifles, unexpectedly turned up last month, apparently driven by efforts in several states to impose gun bans.
Industry officials reviewing the latest FBI background check information said that states planning gun bans or moving to change the rules governing firearms purchases saw massive jumps in April sales.
In Washington state, where the governor just signed a law banning the sale or transfer of AR-style rifles, background checks for April sales surged to 71,272 compared to 49,641 in April 2022, a 43.6% increase, said Mark Oliva, the spokesman for the National Shooting Sports Foundation.
The industry trade group found a surge in Illinois, where it recently won a federal court decision to block a ban on modern sporting rifles. There, Oliva said, sales background checks increased 11.7% in April.

Ditto in Oregon, he said: “Oregon, a state with a legislature and governor’s office hostile to lawful firearm ownership, totaled 43,574 adjusted background checks in April 2023, compared to 27,921 a year ago, representing a 56.1% increase.”
Even states that moved to change the rules to buy guns saw a big sales uptick before any new regulations began to take effect.
“Notably, North Carolina’s legislature overrode Gov. Roy Cooper’s veto of a bill that repealed the state’s antiquated Jim Crow-era permit-to-purchase a handgun scheme which immediately reverted the state to using the FBI NICS system to verify all handgun sales,” Oliva said. “North Carolina came in with 68,181 background checks in April 2023, compared to 18,967 in April 2022, a 238.4% increase.”
In recent months, concerns about safety drove sales highs, and that is continuing to add to the records. But Oliva said the difference in April was the threats from the government to take away gun rights.
SEE THE LATEST POLITICAL NEWS AND BUZZ FROM WASHINGTON SECRETS
“April’s uptick of 1,369,296 FBI National Instant Criminal Background Check System (NICS) verifications shows that there continues to be a steady appetite for lawful firearm ownership even as certain state governors and legislators are taking radical measures to infringe on the Second Amendment rights of law-abiding citizens to possess firearms, especially the Modern Sporting Rifle,” Oliva said in a reference to AR- and AK-style rifles.
“These figures show that when Americans are concerned that government authorities will deny them the full spectrum of their Second Amendment rights, they will respond by exercising those rights. It also shows that when barriers to lawful firearm ownership are torn down, law-abiding citizens will exercise their right to lawfully purchase firearms,” he said.

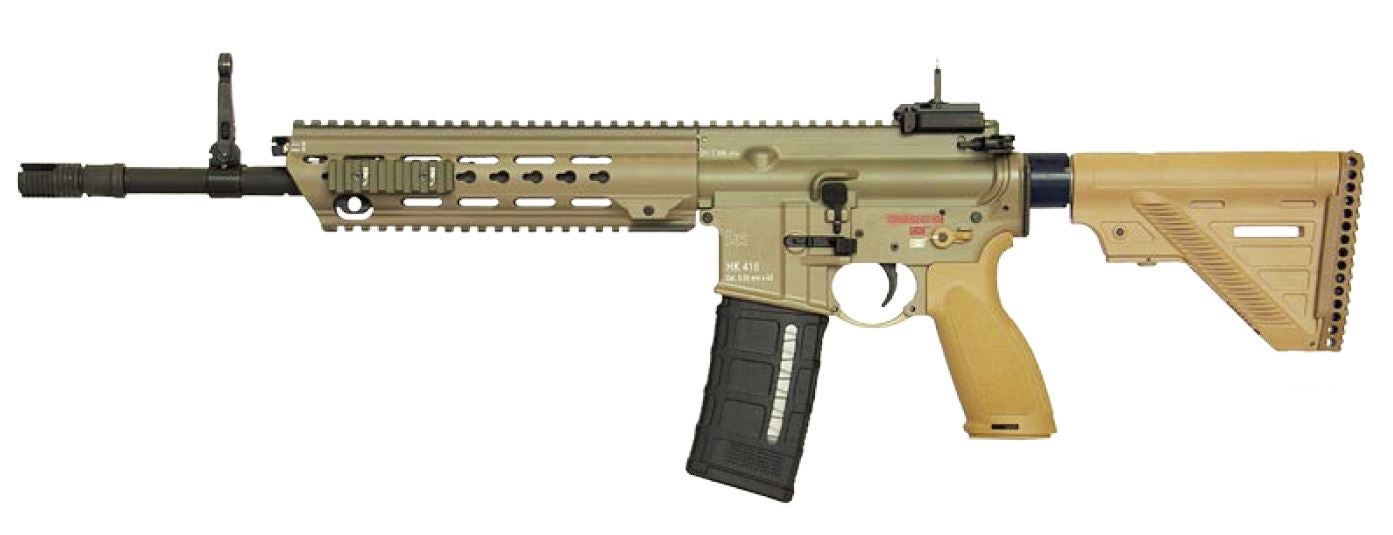
Luxembourg Army Adopts HK416
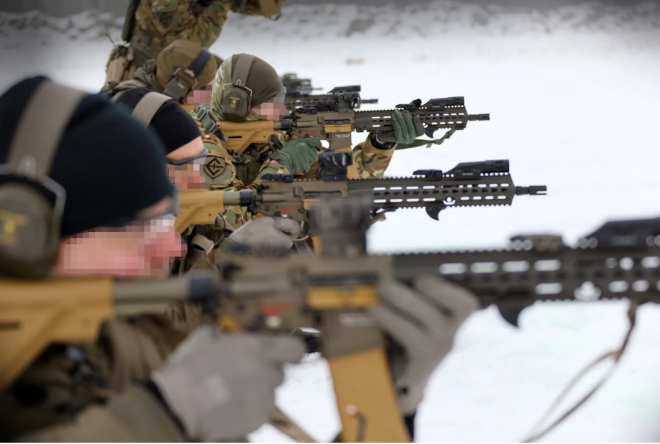

The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg will equip its armed forces with the HK416 A7. Luxembourg will replace the Steyr AUGs currently in service with weapons from Heckler & Koch through a contract worth 8.4 million Euros ($9.2 million).
HK416 @ TFB:
- German Army One Step Closer To Procuring HK416A8
- POTD: Heckler & Koch HK416F with EOTech
- Strike Industries GRIDLOK Handguard Now For HK416
- POTD: Heckler & Koch HK416 with Backup HK MP7
The procurement will also include Heckler & Koch HK269s which will replace older HK69A1s. The 5.56x45mm HK416s will be procured in two barrel lengths: 11 and 14.5 inches. The contract also includes 7.62x51mm HK417 A2 rifles which will likely provide a designated marksman rifle.
The Luxembourg Army is a battalion-sized formation and the latest available figures put Luxembourg’s full-time standing military at just around 1,000 personnel. While Luxembourg’s standing army is small it has provided personnel and equipment to UN, NATO and EU peacekeeping missions since the early 1990s.
The Luxembourg Army has not yet commented on the procurement but HK expects to deliver the rifles by 2024.
Here’s Heckler & Koch’s announcement of the contract:
On 18 April 2023, the Luxembourg army commissioned Heckler & Koch to supply the future standard assault rifle to its armed forces.
In advance to the contract, Heckler & Koch was able to clearly win an intensive comparative test against a well-known European competitor. For about 8.4 million Euros, the army of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg will receive an HK416 A7 assault rifle variant in 5.56 mm x 45 NATO calibre in two different barrel lengths – 11 and 14.5 inches.
The defence package is completed by 40 mm HK269 grenade launcher modules as well as HK417 A2 assault rifles in the NATO calibre 7.62 mm X 51. With this decision, the Luxembourg alliance partner is parting with its Steyr AUG used up to now and, with the HK416, the Luxembourg army is relying on a mission-proven quality product from Heckler & Koch for its soldiers which is widely used in the NATO.
The delivery of the new standard weapon to the Grand Duchy will take place within a year and is scheduled for completion in 2024.
Find out more at www.heckler-koch.com





